
12-Lead ECG (2nd Edition) Edit editionThis problem has been solved:Solutions for Chapter 9
Looking for the textbook?- CH1
- CH2
- CH3
- CH4
- CH6
- CH7
- CH8
- CH9
- CH10
- CH11
- CH12
- CH13
- CH14
- CH15
- CH16
- 1CR
- 1QR1
- 1QR2
- 1QR3
- 1QR4
- 1QR5
- 1QR6
- 2CR
- 2QR1
- 2QR2
- 2QR3
- 2QR4
- 2QR5
- 2QR6
- 3CR
- 3QR1
- 3QR2
- 3QR3
- 3QR4
- 3QR5
- 3QR6
- 4CR
- 4QR1
- 4QR2
- 4QR3
- 4QR4
- 5CR
- 6CR
- 7CR
- 8CR
- 9CR
- 10CR
Electrocardiogram (ECG) comprises of three components – P waves, QRS complexes and T waves. The interval between P wave and QRS complex is termed as P-R interval and the interval between QRS complex and T wave is termed as ST interval.
Each component indicates different activity of the heart. QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization and the T wave represents ventricular repolarization.
Hence, options (C) and (D) are not the correct answers.
Atrial repolarization is not visible as any waveform of ECG as it gets masked in the stronger QRS complex of ventricular depolarization. Thus, P wave do not represent the atrial repolarization.
Hence, option (A) is not the correct answer. Also, the answer given in option (B) is correct and therefore option (E), stating ‘none of the above’ is not correct.
P wave indicates atrial depolarization. P wave is the first wave of the cardiac cycle observed on ECG. The wave starts as soon as it leaves the baseline and ends when it returns to the baseline. The atrial depolarization begins in the SA (sinoatrial node) and spreads through the atria to reach the atrioventricular (AV) node.
Hence, the correct answer is option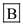 .
.
Corresponding textbook




