
12-Lead ECG (2nd Edition) Edit editionThis problem has been solved:Solutions for Chapter 13
Looking for the textbook?- CH1
- CH2
- CH3
- CH4
- CH6
- CH7
- CH8
- CH9
- CH10
- CH11
- CH12
- CH13
- CH14
- CH15
- CH16
- 1CR
- 1MI7
- 1MII6
- 1MIII5
- 1QR1
- 1QR2
- 1QR3
- 1QR4
- 2CR
- 2QR1
- 2QR2
- 3CR
- 3QR1
- 3QR2
- 4CR
- 4QR2
- 5CR
- 6CR
- 7CR
- 8CR
- 9CR
- 10CR
- 11CR
- 12CR
- 13CR
- 14CR
- 15CR
Left ventricle receives transmission by left bundle if right bundle is blocked. Due to cell-to-cell depolarization caused by block, impulse is delayed to interventricular septum and right ventricle. Delay in impulse causes delay in depolarization time and it can be observed in electrocardiogram (ECG) with an elongated QRS interval to 0.12 seconds. In some cases, it records as an additional wave to that of the existing one forming an RSR′ complex. R′ is the additional wave which is formed due to slow transmission in the interventricular septum and right ventricle.
Generally left ventricle forms a vector accountable for QRS complex. Slow transmission by interventricular septum and right ventricle in Right Bundle Branch Blocks (RBBB) forms a slow vector which is not opposed by left ventricle vector. The new slower vector formed by slow transmission causes a deviation in the ECG. Normally S wave becomes unclear due to slow transmission by interventricular septum and right ventricle which is important in diagnosing RBBB.
As identifying V1 alone does not help in diagnosing RBBB, hence the given statement is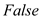
Corresponding textbook




